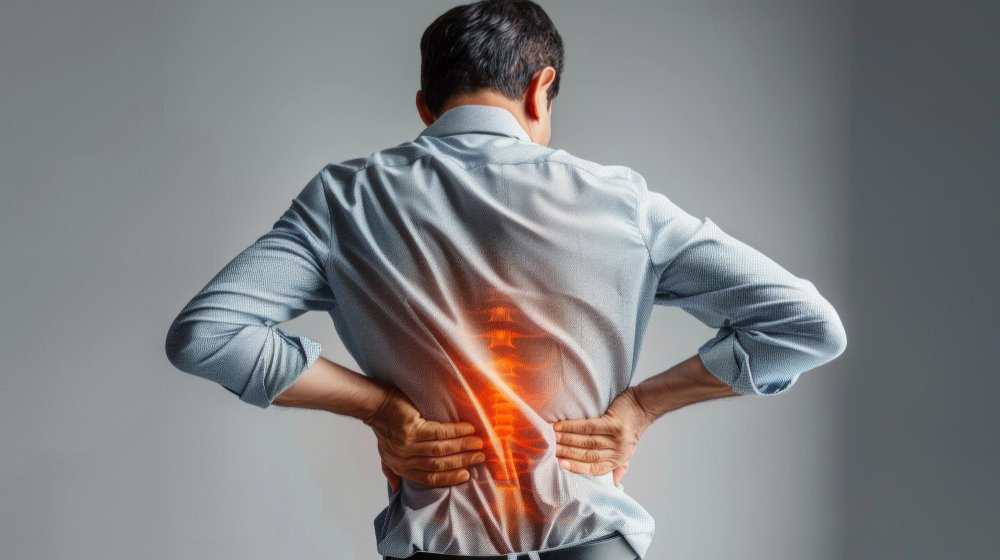
What is Back Pain?
Back pain is a common condition that affects many people. It can vary in intensity from a dull, constant ache to a sudden, sharp pain. Back pain can occur in different areas of the back:
- Upper Back Pain: This occurs in the area between the neck and the bottom of the rib cage. It can be caused by poor posture, muscle strain, or injury.
- Middle Back Pain: Located between the shoulder blades, this type of pain is often related to poor posture, muscle strain, or herniated discs.
- Lower Back Pain: The most common type, affecting the area from the bottom of the rib cage to the top of the legs. It can result from muscle strain, herniated discs, or other conditions.
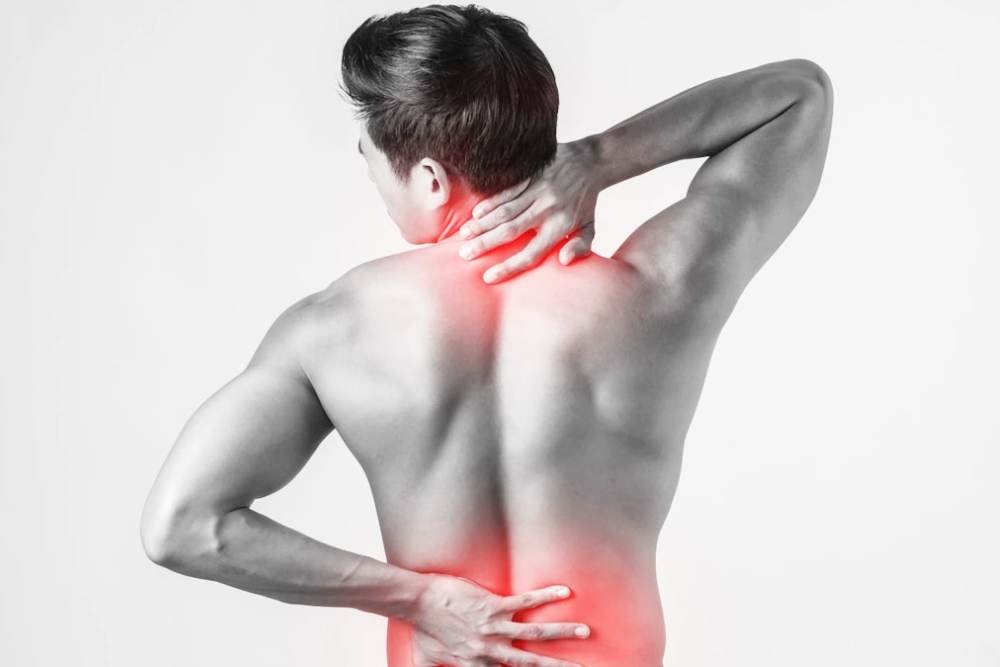
Precautions
To help prevent or manage back pain, consider the following:
- Maintain Good Posture: Sit and stand with your back straight. Avoid slouching or leaning forward for extended periods.
- Exercise Regularly: Strengthening your core muscles, which support your spine, can help prevent back pain. Activities like walking, swimming, and yoga are beneficial.
- Lift Properly: Use your legs, not your back, when lifting heavy objects. Keep your back straight and avoid twisting while lifting.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Extra weight, especially around the abdomen, can strain your back. A balanced diet and regular exercise can help maintain a healthy weight.
- Use Ergonomic Furniture: Ensure your chair and workstation support your back correctly. Adjust the height of your chair so your feet are flat on the floor and your knees are level with your hips.
- Avoid Prolonged Sitting: Take breaks to stand up, stretch, or walk around, especially if you have a desk job.
Treatment
Treatment for back pain depends on the cause and severity. Common treatments include:
- Over-the-Counter Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen (Advil) or acetaminophen (Tylenol) can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can design exercises to strengthen your back, improve flexibility, and correct posture.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying heat or cold packs can help reduce pain and inflammation. Heat is often used for muscle relaxation, while cold can reduce swelling.
- Prescription Medications: For more severe pain, your doctor may prescribe muscle relaxants or stronger pain relievers.
- Alternative Therapies: Treatments such as acupuncture, chiropractic care, or massage therapy may provide relief for some individuals.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Implementing changes like better posture, regular exercise, and weight management can reduce or prevent back pain.
When to See a Doctor
Consult a healthcare provider if:
- You experience severe or persistent back pain.
- Your pain is accompanied by symptoms such as numbness, tingling, or weakness in your legs.
- You have back pain following a fall, injury, or trauma.
- You have unexplained weight loss, fever, or other symptoms that concern you.
Back pain can be uncomfortable and disruptive, but with proper care and management, it’s often possible to find relief and prevent future issues. If you have any concerns or if your back pain persists, seeking advice from a healthcare professional is the best course of action.