DEMYELINATING DISEASES

What are Demyelinating Diseases?
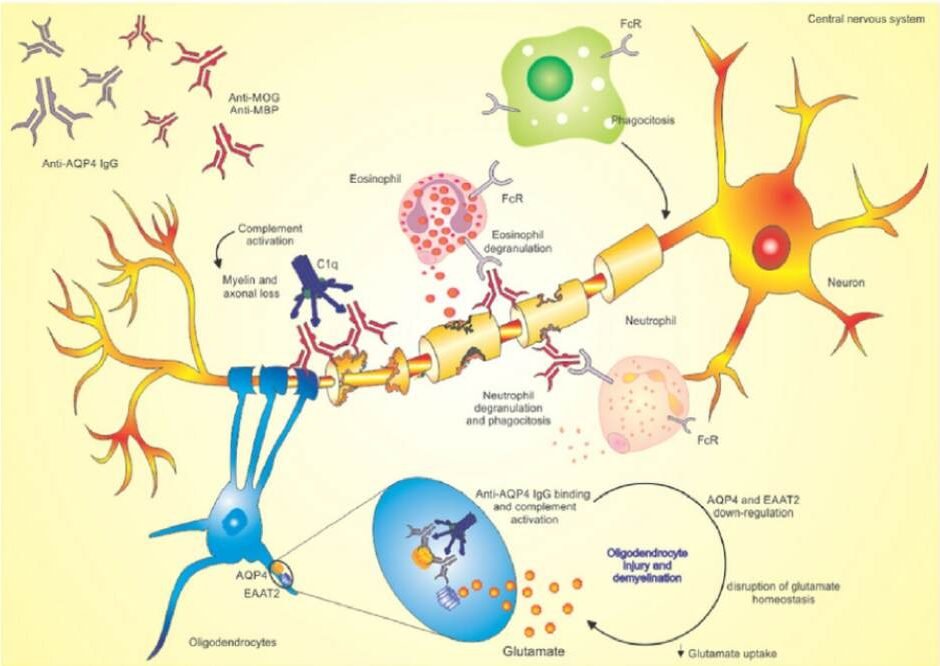
Myelin is protective sheath around neurons of both central and peripheral nervous system. Demyelinating disorders most commonly affect brain, spinal cord, and optic nerves. Demyelination is often secondary to an infectious, an ischemic, a metabolic, or a hereditary disorder or to a toxin (eg, alcohol, ethambutol). In primary demyelinating disorders, cause is unknown, but an autoimmune mechanism is suspected because the disorder sometimes follows a viral infection or viral vaccination.
Multiple sclerosis is a chronic autoimmune disease affecting the central nervous system (CNS) and is characterized by inflammation, demyelination, gliosis, and neuronal loss. This condition manifests with a wide range of clinical manifestations including Vision symptoms such as vision loss, vertigo and gait imbalance, dysarthria and dysphagia, weakness (hemiparesis, monoparesis, or paraparesis), tremors, loss of sensation, paraesthesias, dysesthesias, and a band-like sensation, Urinary and bowel symptoms ranging from incontinence, retention, urgency, constipation, diarrhea, Cognitive symptoms such as memory impairment, facial muscle weakness and/or reduced facial sensations, diplopia, oscillopsia.

Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder primarily targets the optic nerves, brainstem, and spinal cord. Optic neuritis presents with acute onset, painful, monocular vision loss, with a relative afferent pupillary defect in the affected eye, intractable hiccups, unexplained nausea or vomiting, or symptomatic narcolepsy, Acute myelitis.
Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) antibody-associated disease (MOGAD) is the most recently defined inflammatory demyelinating disease of the central nervous system. Clinical manifestations of MOGAD are heterogeneous, ranging from isolated optic neuritis or myelitis to multifocal CNS demyelination often in the form of acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM), or cortical encephalitis.
Prompt evaluation and management of demyelinating disorders can prevent mortality and morbidity
